Mission statement
Collaborating with Drivetrain Experts for Procurement Success

Our unparalleled reliability ensures seamless integration into diverse projects, guaranteeing optimal performance and longevity for your esteemed operations.
Our unmatched flexibility ensures smooth integration into any project, adapting seamlessly to diverse requirements. With agile solutions tailored to your needs, we guarantee optimal performance and enduring success for your operations.

Client satisfaction is paramount. Our customer-centric philosophy means that companies experience personalized attention, streamlined communication, and bespoke solutions.
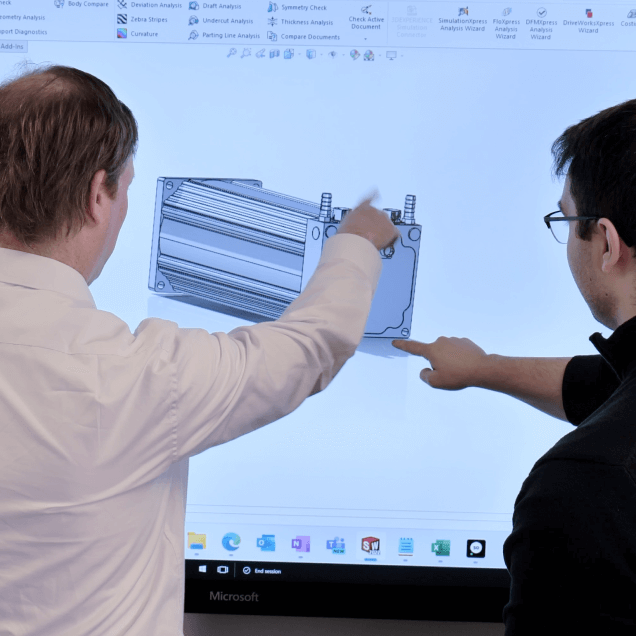
iNetics’ approach to design is inherently focused on manufacturing efficiency, ensuring that every product we create is designed to be produced with precision, cost-effectiveness, and scalability in mind.
We Make Groundbreaking Motor Designs That Set Industry Standards
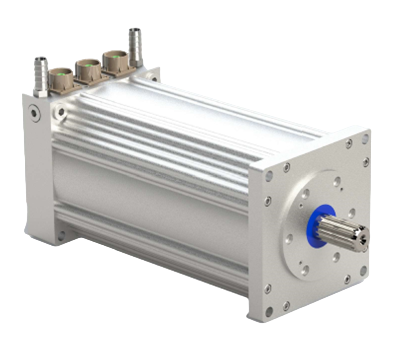
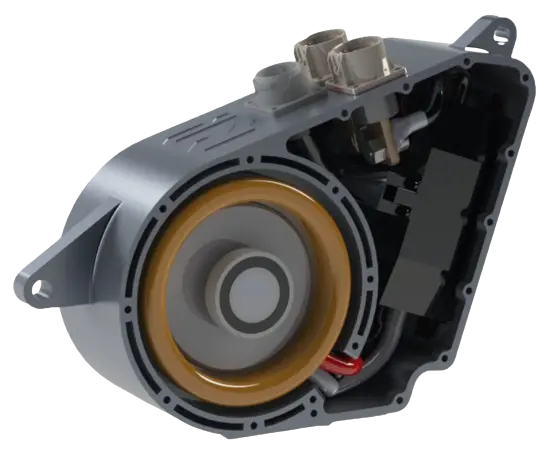
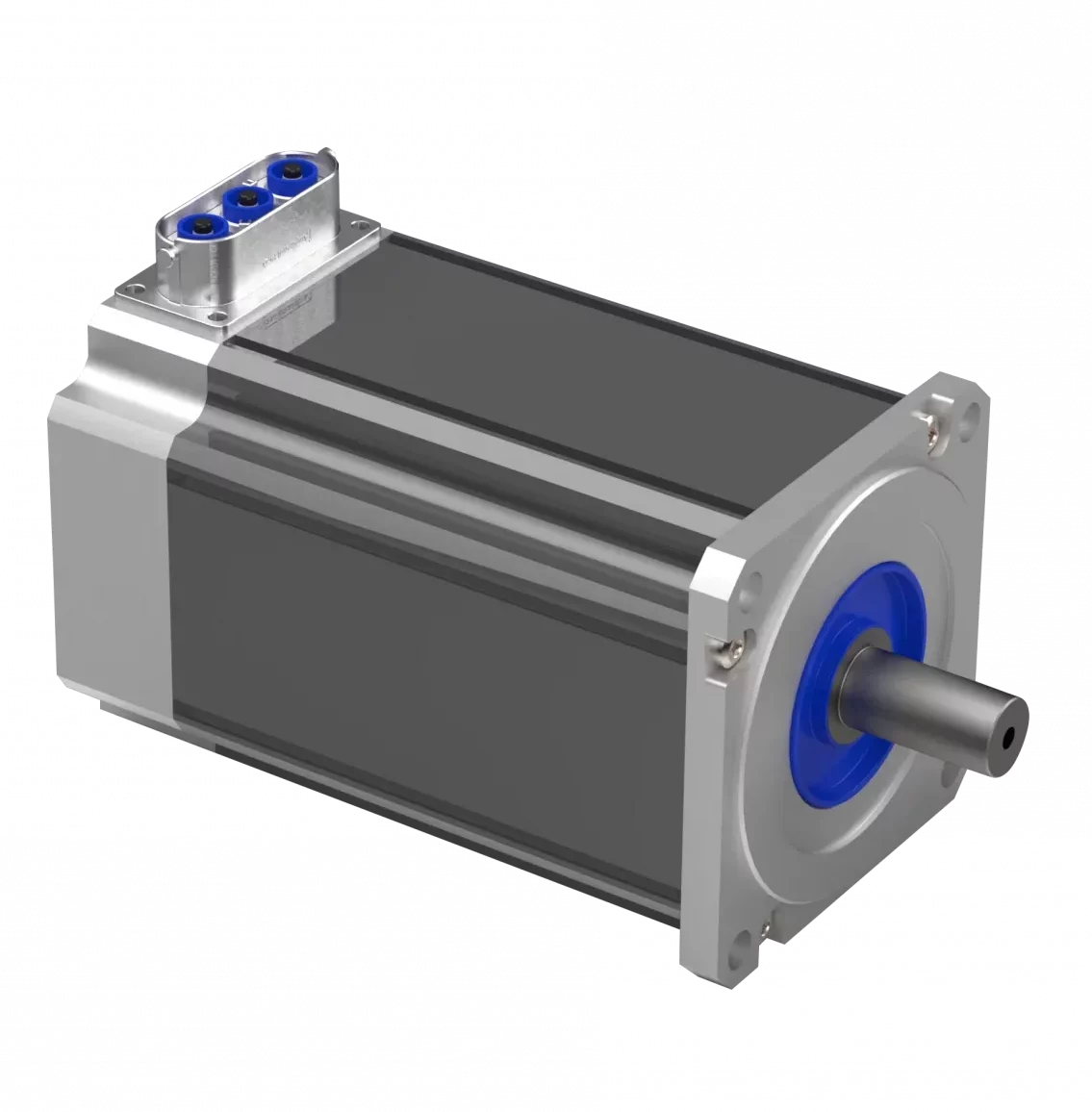
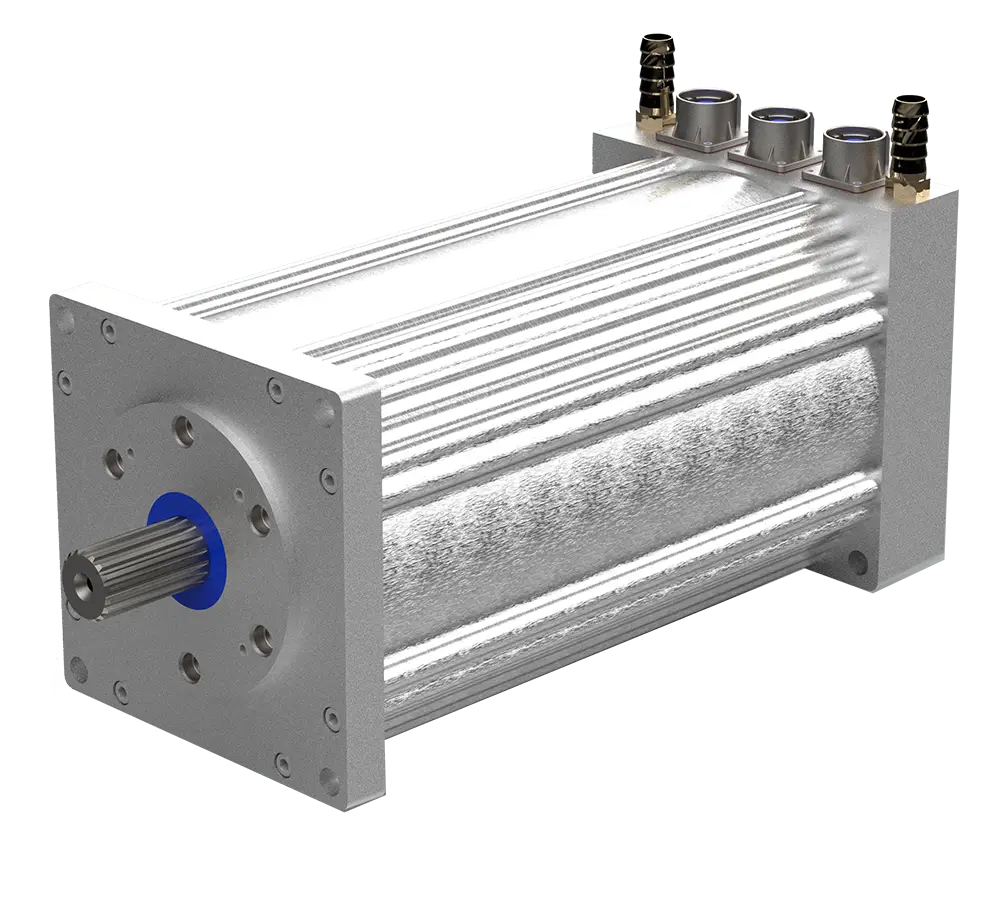
Featured motors available on our shelves
Engineering Insights

MTPA and Manual Phase Angle Sweeping
Achieving maximum efficiency in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) requires precise control of current distribution between the d-axis and q-axis. Maximum Torque Per Ampere (MTPA) ensures the highest torque output for a given current, reducing losses and improving electric vehicle range. While simulation tools provide initial estimates, Manual Phase Angle Sweeping remains essential for accurate real-world calibration—capturing temperature effects, magnetic saturation, and field weakening behavior. This process forms the backbone of reliable inverter tuning and optimal traction motor performance.
Why Marine Electrification Starts with Compliance
Marine electrification promises cleaner, quieter vessels – but bringing electric propulsion to the seas isn’t as simple as dropping a Tesla drivetrain into a ship. The maritime domain is governed by strict regulations and classification society rules that make compliance a foundational design consideration, not an afterthought. In fact, ensuring regulatory compliance from day one is often the only way to turn bold electrification concepts into practical realities on the water. This article explores why compliance comes first in marine electrification, how marine rules shape technical design (from electrical safety and redundancy to EMC and fire protection), and what it means for system-level engineering. We’ll also look at real-world projects (ferries, workboats, offshore vessels) where a compliance-first approach paved the way for success, and conclude with why marine-savvy integration partners are key in this emerging field.
Emerging Battery Technologies
In the quest to surpass conventional lithium-ion batteries, several next-generation chemistries are gaining momentum. Below is a comparative look at four prominent contenders – Lithium-Air, Sodium-Ion, Solid-State, and Semi-Solid-State batteries – focusing on their key characteristics, recent breakthroughs, leading players, commercialization timelines, and technical challenges. A summary table and detailed analysis for each chemistry are provided for a global, engineering-oriented audience.
Why Marine Electrification Starts with Compliance
Marine electrification promises cleaner, quieter vessels – but bringing electric propulsion to the seas isn’t as simple as dropping a Tesla drivetrain into a ship. The maritime domain is governed by strict regulations and classification society rules that make compliance a foundational design consideration, not an afterthought. In fact, ensuring regulatory compliance from day one is often the only way to turn bold electrification concepts into practical realities on the water. This article explores why compliance comes first in marine electrification, how marine rules shape technical design (from electrical safety and redundancy to EMC and fire protection), and what it means for system-level engineering. We’ll also look at real-world projects (ferries, workboats, offshore vessels) where a compliance-first approach paved the way for success, and conclude with why marine-savvy integration partners are key in this emerging field.
Emerging Battery Technologies
In the quest to surpass conventional lithium-ion batteries, several next-generation chemistries are gaining momentum. Below is a comparative look at four prominent contenders – Lithium-Air, Sodium-Ion, Solid-State, and Semi-Solid-State batteries – focusing on their key characteristics, recent breakthroughs, leading players, commercialization timelines, and technical challenges. A summary table and detailed analysis for each chemistry are provided for a global, engineering-oriented audience.